Buy Sampling Products
At OdemShop, we offer a selection of products for various types of sampling. Whether you need a nasal and throat swab or a blood sample, we have the solution.
Sampling method
In this article we will explore all aspects of Art of Sampling. We will look at the theory behind its methodology; discuss different types of sample designs; explain how to select appropriate units for sampling; find out what statistical tests should be used when analyzing the results; consider possible applications for real-world scenarios; and finally, find out if this approach is still relevant today. So if you want to learn more about type of sampling, read on!
What is sampling?
Sampling is the taking of samples (a small amount) of a material from a larger quantity in order to examine, analyze, or test the samples taken.
Many people today wonder how to properly diagnose the possible onset of a disease. A reliable method for this is the sampling of body fluids and tissue samples. This process can take several forms: rapid antigen testing, PCR testing or FOB testing for blood tests, and FOB self-testing and NT-proBNP as a urine test. These methods can be used to obtain accurate information about a specific disease. The diagnostic criteria vary depending on the type of test method - each has its specific areas of application. For example, a nasal and throat swab allows further details about a possible source of infection to be determined.
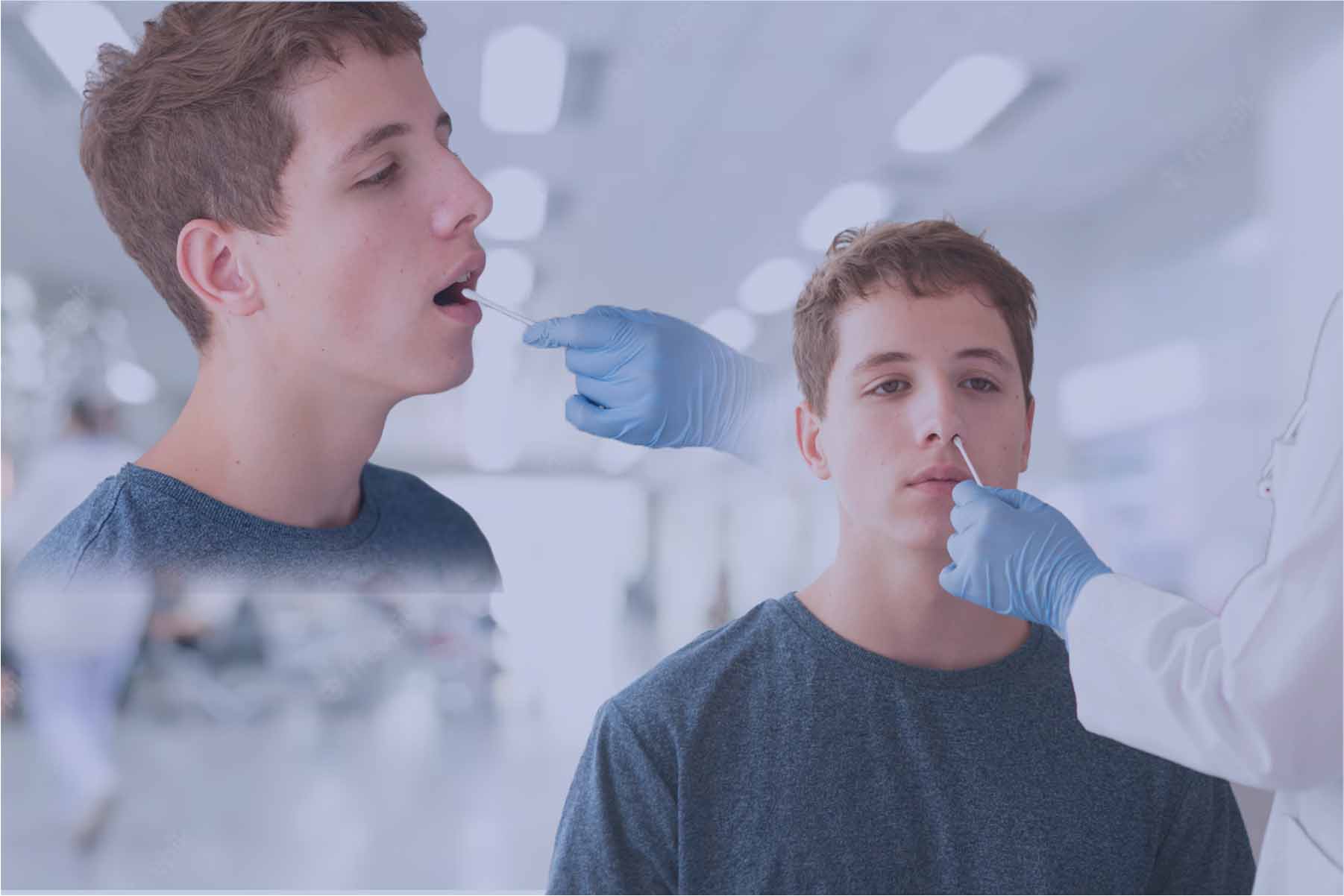
Nasal and throat swab
The nasal and throat swab is one of the common methods of sampling to determine the presence of coronavirus. For this, a cotton swab is inserted into the back of the nose or inhaled. The cotton swab is then placed on a slide for microbiological testing to determine virus particles. In addition, the swab can be used for combination tests to diagnose various infections, such as Corona self-tests, which are very popular nowadays. There are also some FOB self-tests that allow patients to have their results sent home. Some tests can also detect specific values, such as D dimer or CK MB.
However, the nasopharyngeal swab does not guarantee 100% accuracy. This is because some people produce more secretions than others, so further testing may be necessary to get accurate results with this sampling. In addition, bacteria may be found in the sample material instead of viruses, which can also cause inaccurate test results. Therefore, extra care should be taken when choosing a test and the proper information should be gathered before going to the doctor or doing a self-test. Next, we examine the urine to determine if it contains evidence of a specific disease or a deviation from the body's normal function.
Urine tests as sampling
It is a common assumption that urine tests provide reliable results. To verify this, we examine the method of sampling urine, liquid samples, and their role in the validity of the results. Nasal and throat swabs can also be used for certain tests, but because they are usually very invasive, we limit our discussion here to urine samples.
Urine samples are used to diagnose and track a variety of diseases. Examples include micro albumin, FOB self-test, and other routinely prescribed tests. Because collecting a urine sample is relatively easy, this method is the first choice. However, the sample must be collected correctly so that the results are not erroneous or incomplete. In addition, all necessary pre-analysis measures must be taken into account, especially when transporting the material to the laboratories. This helps to ensure trouble-free results.
Therefore, careful study of the sampling method is crucial to extract accurate information from the test material. Thanks to the use of state-of-the-art technologies both in the laboratory and in the collection of the material at the point of care (PoC), it is now possible to obtain precise diagnostic results with high accuracy and reliability. This opens up new avenues for effective treatment of patients - which ultimately serves our common goal: health for all people. Next up is stool testing.
Stool tests
Stool testing is another important test that people can perform. There are several methods of sampling, from FOB self-testing to testing in laboratories or doctors' offices. The advantage of the FOB test is that it is quick, uncomplicated and does not require special instructions. In laboratories and medical practices, a special kit is usually used to be able to take samples. Usually, it is a sterile container filled with a solution that is used to analyze the stool.
This type of analysis offers many advantages: it can help diagnose diseases earlier than would otherwise be the case; it provides information about dietary habits; and finally, it can help assess potential risks. So, with the help of such tests, it is possible to find out what changes should be aimed for - under medical supervision, of course! Now we are faced with blood tests - which we will now discuss in more detail.
Blood tests
Blood tests are one of the most effective methods as sampling to detect diseases. They can be performed on a variety of occasions to monitor a patient's health and identify potential problems. There are many different types of blood tests, but here are some of the most common:
Laboratory analysis: this is the most common type of test, in which a drop of blood is taken from the finger or vein in the arm and analyzed in a laboratory. The test results can provide information about the general condition of the body; cholesterol levels, sugar levels, and inflammatory markers are determined.
Radiological tests: These include X-rays and computerized tomography (CT) scans. These procedures help you examine internal organs and identify any tumors or other findings.
Endoscopic tests: these are invasive procedures using specially made instruments that are used to remove tissue samples for diagnosis of disease or deviations from normal. Examples include colonoscopies (colonoscopy) or bronchoscopies (lung), which are performed directly inside the patient's body.
It is therefore up to the medical staff to weigh up whether a particular type of sampling is particularly suitable and to what extent this procedure should be used - after all, this is the only way to respond optimally to individual needs. Advantages are fast results, precise data collection and high safety standards, but disadvantages such as high investment, time-consuming process and possible risk of side effects and allergies, must also be considered.
Frequently asked questions
What is sampling?
Sampling is the process of taking a sample of a material or fluid to test for the presence of infectious agents or other substances.
What types of samples can be taken for infection testing?
Several types of specimens can be used for infection testing, including blood, urine, stool, nasal and throat swabs, and saliva.
What is a nasal swab?
A nasal swab is a type of specimen collection in which a long swab is inserted into the nostril to collect a sample.
What is a throat swab?
A throat swab is a type of sampling in which a long swab is inserted into the throat to collect a sample.
How are urine samples collected?
Urine samples are usually collected by urinating into a cup or special container.
How are stool samples collected?
Stool specimens are usually collected by emptying stool into a special container.
What preparations are needed to collect a specimen?
Depending on the type of sample, different preparations may be required, such as fasting or avoiding certain foods or medications.
How is a nasal sample collection performed?
This sample collection is usually performed by inserting a long swab into the nostril and gently passing it through the nasal cavity to the throat.
How is a throat sample collection performed?
A throat sampling is usually performed by inserting a long swab into the throat and carefully taking a sample.
Are nasal and throat swabs painful?
Nasal and throat swabs can be uncomfortable, but they should not be painful.
How is a blood sample taken?
A blood sample is usually taken by drawing a small amount of blood from a vein in the crook of your arm.
Are blood tests painful?
A blood sample may cause a slight stinging or burning sensation when the needle is inserted, but it should not be painful.
Are urine samples painful?
Urine samples should not be painful.